Key Takeaways
- UV radiation can damage your skin, eyes, and immune system – even on cloudy days.
- Too much exposure to UV rays can increase the risk of skin cancer, cataracts, premature skin aging, and can weaken your immune system.
- Wearing sunscreen, protective clothing, and sunglasses can reduce the risk of UV radiation overexposure.
No matter the season, being outside often means being in the sun – and that also means being exposed to ultraviolet (UV) rays.
UV exposure increases with sunlight, which means the higher the sun is in the sky, the higher the level of UV radiation. UV levels are generally at their highest levels between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. in the summer months.
Like most things, UV rays are best if absorbed in moderation. We explain some of the potential harms of UV overexposure and the best ways to avoid too much UV radiation.
How UV radiation harms your body
If you end up absorbing too much UV radiation, it can increase certain health risks in several ways.
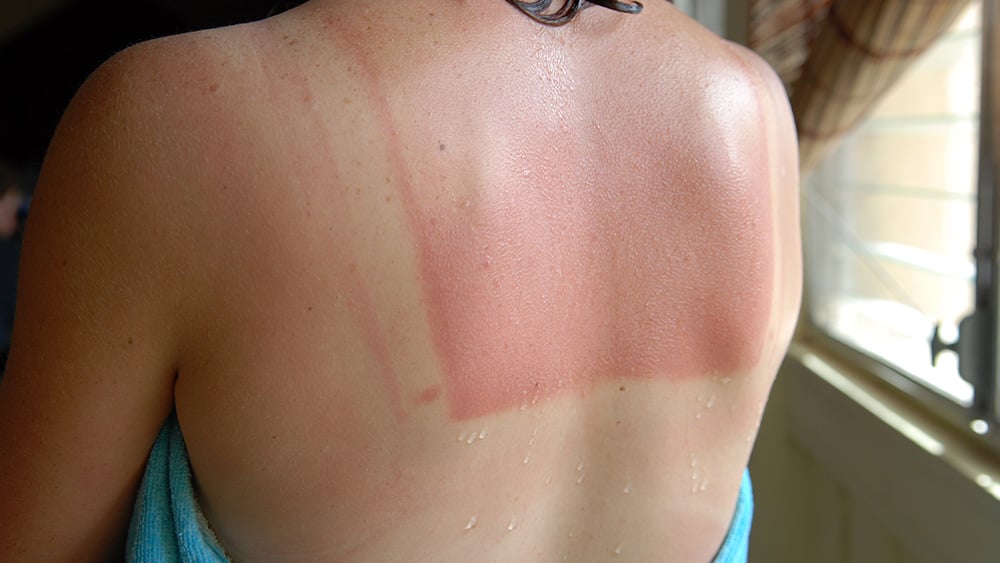
Skin cancer: Too much exposure to UV rays can raise your risk of developing skin cancer, according to the American Cancer Society.
Protecting yourself against exposure to UV radiation is the easiest way to prevent skin cancer.
Premature skin aging: If you’re outside frequently without any sort of protection from sunscreen or clothing, your skin can burn and dry out more quickly. This leads to skin aging more rapidly; as much as 90 percent of visible skin changes linked to aging are from sun damage.
Cataracts: Cataracts develop when the lens inside the eye becomes less transparent and clouds your vision. Studies suggest UV radiation raises the risk of some cataracts.
Wearing UV-blocking sunglasses protects your eyes (and the skin around them) from taking in too much UV light.
Suppressed immune system: Research shows the more someone is exposed to UV radiation, the more their immune system is suppressed. If your skin is absorbing more UV rays, it is less likely to protect itself against infections.
How to stay protected from UV rays
Stay in the shade: Perhaps the most straightforward way to steer clear of UV rays is to stay indoors or in shaded areas. If you are going to be outdoors, stay under an umbrella, tree canopy, or other covered area away from the sun.
Wear protective clothing: When dressing to be outdoors in the sun, think of the areas of your skin that will be exposed to sunlight. Wear a hat, long-sleeved shirt, and/or something that protects your neck to get the most protection possible.
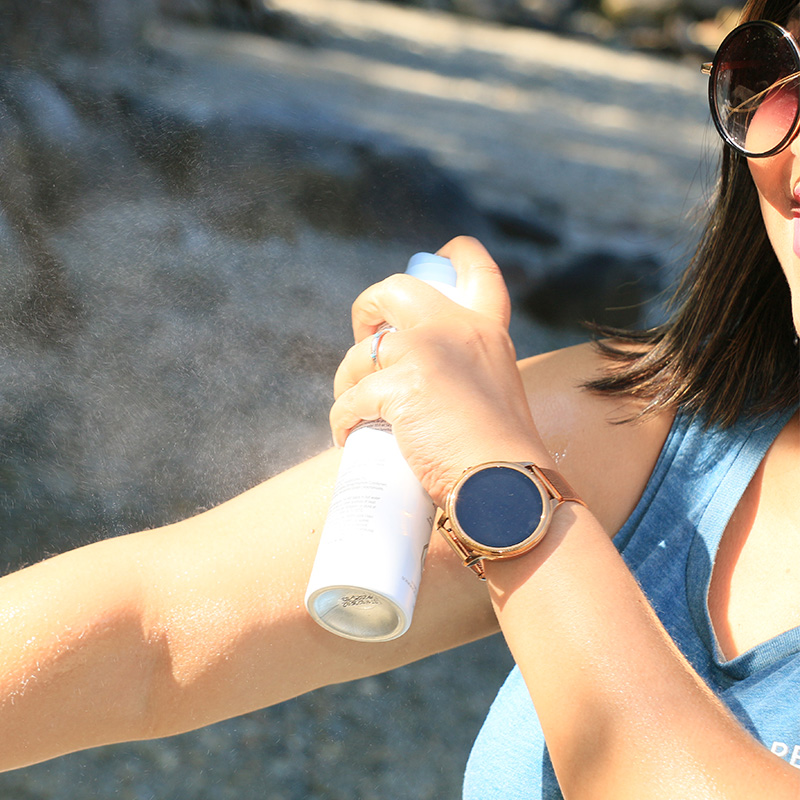
Wear sunscreen: Sunscreen is a simple but effective way to protect your skin against sun damage. Dermatology experts suggest wearing a sunscreen with at least SPF30 protection and reapplying every two hours. View our sunscreen recommendations and how to apply properly.
Wear sunglasses: Sunglasses not only make you look cool – they also protect your eyes and the skin around them from UV rays. As previously mentioned, UV radiation raises the risk of eye damage and cataracts, so putting on a pair of UV-protected sunglasses is a good idea.
Don’t use tanning beds: The UV rays given off by tanning lamps and beds raise your risk of skin cancer and have been linked to a higher chance of developing skin cancer. Consider other ways of tanning instead.
If you are concerned about skin damage or an abnormal spot on your skin, our dermatology and skin care providers are available to help you get the answers you need.